![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
This site is designed to be viewed on an
800 x 600 screen,
with level 4+ browsers.
Created by Andy Darvill,
Science teacher at
Broadoak Community School,
Weston-super-Mare, England
Web site www.darvill.clara.net
Introduction How it works More details Advantages Disadvantages Is it renewable?
![]()
Introduction
|
We have used running water as an energy source for thousands of years, mainly to grind corn. The first house in the world to be lit by hydroelectricity was Cragside House, in Northumberland, England, in 1878. In 1882 on the Fox river, in the USA, hydroelectricity produced enough power to light two paper mills and a house. Nowadays there are many hydro-electric power stations, providing around 20% of the world's electricity. The name comes from "hydro", the Greek word for water. |
 |
![]()
How it works
|
A dam is built to trap water, usually in a valley where there is an existing lake. Water is allowed to flow through tunnels in the dam, to turn turbines and thus drive generators. Notice that the dam is much thicker at the bottom than at the top, because the pressure of the water increases with depth. |
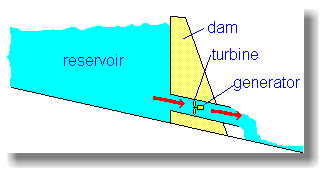 |
 |
Hydro-electric power stations can produce a great deal of power very cheaply. When it was first built, the huge "Hoover Dam", on the Colorado river, supplied much of the electricity for the city of Las Vegas; however now Las Vegas has grown so much, the city gets most of its energy from other sources. There's a good explanation of how hydro power works at www.fwee.org. Although there are many suitable sites around the world, hydro-electric dams are very expensive to build. However, once the station is built, the water comes free of charge, and there is no waste or pollution. |
|
The Sun evaporates water from the sea and lakes, which forms clouds and falls as rain in the mountains, keeping the dam supplied with water. |
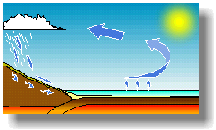 |
![]()
More details
 |
Gravitational potential energy is stored in the water above the dam. Because of the great height of the water, it will arrive at the turbines at high pressure, which means that we can extract a great deal of energy from it. The water then flows away downriver as normal. In mountainous countries such as Switzerland and New Zealand, hydro-electric power provides more than half of the country's energy needs. An alternative is to build the station next to a fast-flowing river. However with this arrangement the flow of the water cannot be controlled, and water cannot be stored for later use. See also: www.fuelfromthewater.com |
![]()
Advantages
|
 |
![]()
Disadvantages
|
 |
Is it renewable?
Hydro-electric
power is renewable.
The Sun provides the water by evaporation from the sea, and will keep
on doing so.
![]()
|
|
|
Want
to discuss alternative energy issues? |